Oil pressure gauges are an invaluable asset that help ensure proper engine lubrication and optimize fuel efficiency, as well as alert drivers to any abnormalities that require attention.
An oil pressure gauge is a transparent cylindrical device with a needle moving across its dial that measures oil pressure through one of the major oilways near to pumps and filters.
How Oil Pressure Gauges Work
Oil pressure gauges in your car are essential tools that allow you to ensure that the engine and other systems are operating at their peak performance. Understanding how they function will allow you to detect issues early and address them before they cause major disruptions.
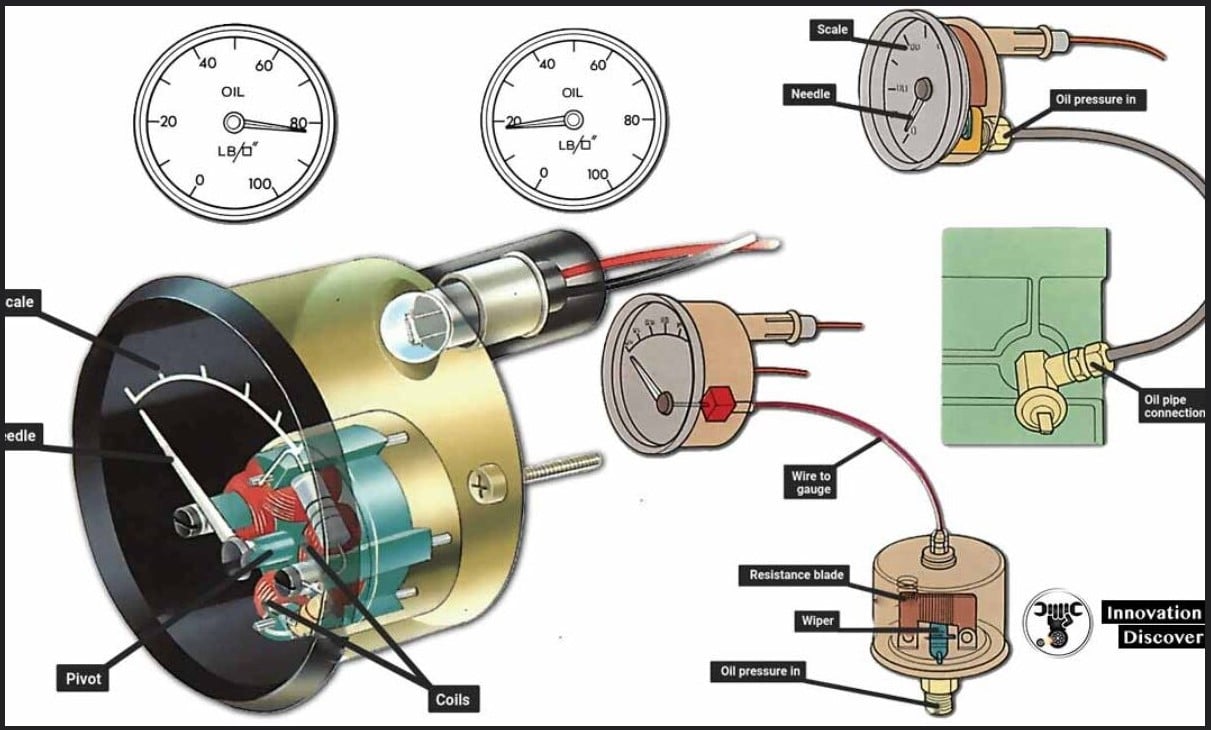
An electric oil pressure gauge features a sensor which sends an electronic signal directly to its gauge. The sensor is located near the oil filter and measures oil pressure before sending this information over. Once received, the gauge displays it on its face.
Mechanical oil pressure gauges use a Bourdon tube that connects one end to fluid while sealing off the other, with one end connected to fluid and one sealed off for sealing purposes. As soon as fluid or gas expands in the tube, it pushes a lever which in turn moves the pointer of the gauge, showing pressure as indicated on its dial gauge.
How to Read an Oil Gauge
Mastering how to read your heating oil gauge is one of the most indispensable skills a homeowner can learn, helping ensure they never run out during a cold snap. By understanding its meaning and use properly you can ensure your home receives enough heat throughout winter.
Most modern vehicles use electric gauges that send an eclectic current through a coil and measure resistance in its return wire to determine oil pressure. These gauges are much easier to integrate into a vehicle’s circuitry and don’t experience wear and tear like mechanical ones do.
Traditional mechanical gauges feature a float which rises when the tank is full, and pushes an indicator needle upward when oil levels decrease – they are not as precise as their electrical counterparts.
Different Types of Oil Pressure Gauges
There is an array of oil pressure gauges to choose from, each offering their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Depending on your application, one type may prove more suitable than others for your vehicle, boat, or equipment.
Electric oil pressure gauges utilize electronic sensors to detect and display oil pressure. While more complex than mechanical gauges, electric oil pressure gauges typically cost more. Mechanical gauges rely on Bourdon tubes to sense pressure before moving a needle on a dial that displays the amount of pressure. Both types can be used to monitor engine oil pressure; regular fluctuations should be expected while sudden spikes or drops could signal problems that require immediate action.
Oil Pressure Gauge Applications
Oil pressure gauges can help ensure that your vehicle or equipment stays in top shape, avoiding catastrophic failures that cost hundreds of dollars in repairs and can cost time and productivity to repair. They also notify you quickly about smaller issues which could be resolved more efficiently with timely action taken immediately.
Mechanical gauges typically use liquid fills such as glycerine-water mixture or silicone oils to help minimize vibration, shock loading and make their needle more resistant to sudden pressure changes.
Electric gauges utilize a sensor attached to the engine block that pushes against a diaphragm inside of it, moving its resistance blade up or down as a wiper moves up or down on it – this in turn changes resistance readings within the gauge, which in turn changes pressure readings, shifting needle accordingly.
Troubleshooting Oil Pressure Gauge Issues
Maintaining an efficient oil pressure gauge is one of the key ways you can keep your engine running smoothly, saving both money and preventing costly repairs or further engine damage. By conducting regular inspections, calibrations, and cleaning sessions on your gauge you can help protect yourself against costly repairs as well as possible future engine problems.
The oil pressure gauge is connected to an oil pressure sensor that may either be mechanical (such as using a coiled tube to transmit oil pressure) or electronic (with sensors that send signals through wire-wound coils). As your engine runs, its internal resistance changes, altering what signal the oil pressure gauge receives and interprets as its readings.
Oil Warning Lights
When your engine’s oil warning light (typically depicted by a red oil can) flashes on, this indicates it has not received enough lubrication – something which could become increasingly problematic as engine parts require sufficient lubrication while running to avoid friction and heat build-up that could ultimately damage them.
The light typically illuminates when your oil pressure falls too low; however, it could also indicate something is amiss with either the gauge itself or oil pump itself. In such instances, professional diagnostic tests must be conducted immediately to identify and rectify the cause of the problem and implement repairs immediately.